Driver Vehicle Standards Agency

4.1.1. Presence, condition and operation
A motorcycle or motorcycle and sidecar must be fitted with one headlamp, although additional headlamps may be fitted. Apart from headlamp security, the check only applies to mandatory lamps.
Headlamps are not needed on motorcycles that:
- are not fitted with front and rear position lamps
- have had their front and rear position lamps permanently disconnected, painted over or masked
- were first used before 1 January 1931
A motorcycle does not need a main beam headlamp if it:
- was first used before 1 January 1972 and has an engine capacity of less than 50cc
- has a maximum speed up to 30mph or 50km/h
On twin headlamp systems, one or both headlamps may operate on either beam.
Headlamps colour must be one of the following:
- white
- yellow
- mainly white light with a blue tinge
If the light intensity of the lamp is significantly reduced, it should be failed.
If the motorcycle does not have a battery or the battery does not have enough charge, you must run the engine to be able to inspect the headlamps.
A light source means any bulb, LED or other means of emitting light.
You must assess damaged or repaired lamps for security, colour, light output and durability.
| Defect | Category |
|---|---|
| (a) A headlamp: (i) with up to light sources not functioning in the case of LED (ii) missing, inoperative or more than not functioning in the case of LED | Minor Major |
| (b) Headlamp reflector or lens: (i) slightly defective (ii) seriously defective or missing | Minor Major |
| (c) Headlamp not securely attached | Major |
4.1.2. Headlamp alignment
All dipped beam headlamps must be inspected for headlamp alignment.
The type of headlamp will determine whether the aim must be checked on dipped or main beam (see Diagrams 1, 2 and 3).
You can pass a flat top or other alternative dipped beam headlamp, as long as all of the beam upper edge, including any peak is contained within the tolerance band.
You can pass a right hand dip headlamp fitted with masks or converter kits that temporarily alter the lamp for use in the UK by removing the beam kick-up to the right.
If a motorcycle does not have a battery or the battery does not have enough charge, you must run the engine to be able to inspect the headlamp alignment.
The light intensity may be low if the motorcycle is fitted with automatic transmission, but any hot spot can usually still be identified.
How to inspect a headlamp
Using a rail mounted headlamp aim tester:
Position the motorcycle on the designated headlamp aim standing area.
With an assistant sitting on the motorcycle in the normal riding position and holding it in an upright position, align the beam tester with the longitudinal axis of the motorcycle. Then align the centre of the collecting lens with the centre of the headlamp as per the aim tester equipment manufacturers instructions.
Determine the appropriate headlamp beam image and its aim (see Diagrams 1, 2 and 3).
Switch on the appropriate headlamp beam.
Follow the aim tester equipment manufacturers instructions.
Using a headlamp aiming screen:
Position the motorcycle on the designated headlamp aim standing area with the headlamp lens the appropriate distance away from the aiming screen, and its longitudinal centre line at a right angle to the screen.
With an assistant sitting on the motorcycle in the normal riding position and holding it in an upright position, align the screens vertical zero line with the motorcycle headlamps centre line.
Align the horizontal zero line with the horizontal axis of the headlamp using the headlamp height measuring equipment.
Determine the appropriate headlamp beam image and its aim (see Diagrams 1, 2 and 3).
Switch on the appropriate headlamp beam and check the aim on the screen.
For complex lens systems - meaning those that have more than one lamp behind a single lens - make sure the test equipment is aligned exactly on the centre of the dipped beam pocket.
You must not carry out repairs during an MOT test, but you can make minor adjustments to the headlamp aim.
European type - check on dipped beam
European type lamps have an asymmetric dipped beam pattern with:
- a horizontal cut-off on the right
- a wedge of light above the horizontal towards the left, known as the kick up
European type lamps might have a European approval mark, usually a letter E in a circle or an e in a rectangle.
For a European type lamp to pass, you must make sure:
- any kick up is visible on the screen
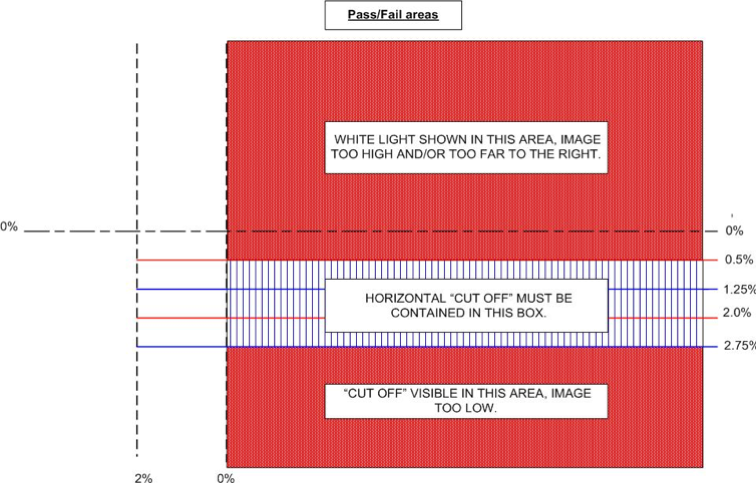
- the beam image horizontal cut-off is between 0.5% and 2.75% below the 0% horizontal line (for headlamps with centres at 850mm or less from the ground)
- the beam image horizontal cut-off is between 1.25% and 2.75% below the 0% horizontal line (for headlamps with centres more than 850mm from the ground)
- white light does not show in the zone formed by the 0% vertical and 0.5% horizontal line
Diagram 1. Criteria for European beam headlamp aim
British American headlamp - check on main beam
Check British American type headlamps on main beam if they have:
- a symmetrical main beam pattern with a central area of maximum intensity (hot spot)
- a circular lens which might be marked with a figure 1 followed by an arrow indicating the direction of dip
You must fail a British American type lamp if its hot spot centre is any of the following:
- above the horizontal 0% line
- below the horizontal 2% line (for headlamps with centres at 850mm or less from the ground)
- below the horizontal 2.75% line (for headlamps with centres more than 850mm from the ground)
- to the right of the vertical 0% line
- to the left of the vertical 2% line
For a British American type lamp to pass, you must also make sure the brightest part of the image moves downwards when the lamp is dipped.
Diagram 2. British American headlamp - Main beam image
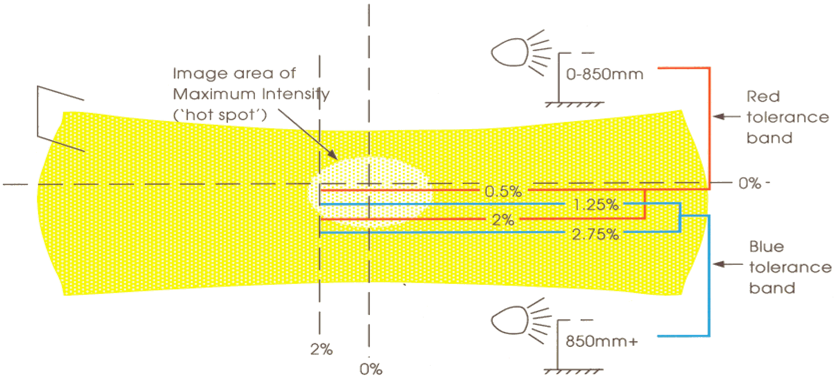
Check the position of the centre of the area of maximum intensity (hot spot)
British American headlamp - check on dipped beam
Check British American headlamps on dipped beam if they have:
- an asymmetric dipped beam pattern which when correctly aimed has a flat-topped area of high intensity extending above and parallel with the horizontal 0% line on the nearside
- a circular lens marked with the figure 2 (it might also have an arrow showing the direction of dip)
You must fail this lamp if the upper edge of the hot spot is:
- above the horizontal 0% line
- below the horizontal 2.75% line
You must fail this lamp if the right-hand edge of the hot spot is:
- to the right of the vertical 0% line
- to the left of the vertical 2% line
Diagram 3. British American headlamp - Dipped beam image

Not tested or unable to be tested should only be used where it becomes apparent during the test that the particular item cannot be tested, and this could not have been identified prior to starting the test. The reason for selecting the failure must be included in the additional information box.
| Defect | Category |
|---|---|
| (a) The aim of a headlamp is not within limits laid down in the requirements | Major |
| (b) Headlamp aim unable to be tested | Major |
| (c) Beam image obviously incorrect | Major |
4.1.3. Switching
All headlamps must light up immediately when theyre switched on.
Some motorcycles do not have a headlamp on switch and the headlamps light up automatically when the ignition is switched on or the engine is started.
Headlamps must switch immediately between main beam and dipped beam when you operate t
